
- #EXCHANGE 2010 ROLES UPGRADE#
- #EXCHANGE 2010 ROLES TRIAL#
- #EXCHANGE 2010 ROLES LICENSE#
- #EXCHANGE 2010 ROLES OFFLINE#
#EXCHANGE 2010 ROLES OFFLINE#
The main role of this role is responsible for loading mailbox databases and public folder databases responsible for generating offline address books and management based on mailbox database levels such as address lists and mail retention policies. When the network scale is small, this role can be deployed on the same server as the CAS role. As long as multiple hub transport role servers are deployed in the same AD site, the multiple servers can automatically achieve load balancing.ĭeployment requirements: This role, like the CAS role, must exist in the Exchange mail system and be added to the AD DS domain. High availability requirements: The high availability of the hub transport role does not need to be configured separately. If the Edge Transport server role is installed, this role is responsible for mail outside the Internet, but the Hub Transport role is always responsible for mail inside the organization. If the Edge Transport server role is not installed, the Hub Transport role will also Forward and receive Internet mail.

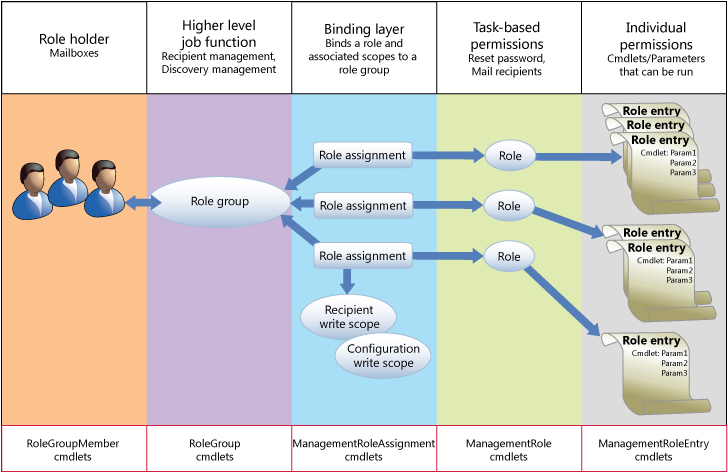
Within the organization, the Hub Transport role is responsible for mail transmission between different MBXs. The main role of the Hub Transport role is to complete applications such as mail delivery, mail transmission rules, and mail log rules. High availability requirements: Regarding the high availability of the client access server role, Microsoft recommends the use of hardware devices, but in small and medium-sized enterprises, Windows NLB can also be used.ĭeployment requirements: This role must exist in the Exchange mail system and must be added to the AD DS domain.
But in Exchange 2010, all client access requests must be connected to the CAS server, and after authentication, they are forwarded to the corresponding mailbox server through the proxy. In Exchange 2007, if the client is using Outlook, then customers can use to connect to the mailbox server, but if they use other methods to access the mailbox, such as POP3, OWA, IMAP4, Activesync, etc., they cannot directly access the mailbox Server, they are directly connected to the client access server, and then this server then locates the user to the mailbox server. Compared with the CAS role of Exchange 2007, the CAS role of Exchange 2010 has undergone a lot of changes. But friends who have been in contact with Exchange Server 2013 may know that the role in Exchange 2013 will change, but this is something later, and I will have the opportunity to talk in detail in the future.įrom the name, you can see that this is the role that handles client access requests. The five roles used are: Client Access Server Role (CAS), Hub Transport Role (HT), Mailbox Database Role (MBX), Edge Transport Server Role (EDGE), and Unified Communication server role (UM). Let's first understand the architecture of Exchange Server2010.Įxchange 2010 is basically the same as Exchange 2007 in terms of architecture. Starting from understanding the Exchange Server 2010 architecture, we will successively introduce its deployment, role configuration management, mail\mailbox management, backup and recovery, high availability, and Exchange migration. This series of articles will take Exchange Server 2010 SP1/SP2 as an example. Enterprise users can download and use it as needed. On the basis of Exchange Server 2010 SP1/SP2, Microsoft officially released the SP3 that supports the installation of Windows Server 2012 on February 12, 2013.
#EXCHANGE 2010 ROLES TRIAL#
In other words, you can use a valid product key to move from the trial version to the standard or enterprise version or from the standard version to the enterprise version or to change the product key on the same version.
#EXCHANGE 2010 ROLES UPGRADE#
The product key can only be used for the exchange and upgrade of the same version key the product key cannot be used for downgrade.
#EXCHANGE 2010 ROLES LICENSE#
And two license versions defined by the product key. The Enterprise Edition can support 100 databases per server the Standard Edition is limited to 5 databases per server.
Exchange Server 2010 is divided into Standard Edition and Enterprise Edition.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
